What is Investment Banking
Investment banking is concerned with aiding corporations, governments and investors with large and complex financial transactions.
It is a demanding profession that requires a top-tier education in finance and a great deal of analytical, critical thinking and mathematical skills. Knowing more about this profession can help you decide if you want to pursue this career.
In this article, we discuss how to become an investment banker, learn what these professionals do on a day-to-day basis and answer some frequently asked questions about this profession.


The course has been structured to give you the practical hands on along with the theoritical class
How to become an investment banker
-
1. Complete 10+2
You need to clear your higher secondary education (10+2) with more than 50% marks from a recognised board. You can opt for the arts, commerce or science stream in your 10+2. Although, you may benefit more from choosing the commerce stream and studying mathematics, accountancy, economics, business and computer technology. -
2. Earn a bachelor's degree
To gain an entry-level position with an investment bank, you need to earn a three or four-year bachelor's degree. You can get a Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com.), a Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) in finance, a Bachelor of Arts (B.A.) in economics and a Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) in finance. While the exact syllabus is different for each programme, you may cover subjects like mathematics, accounting, economics, financial management, corporate finance, investment, taxation, data analytics and business administration. -
3. Join HICM Institute
We are India’s no 1 Investment Banking and Fund Accounting Training Institute.
What is the Investment Banking Division (IBD)?
Core investment banking activities
-
1.Front Office
It is generally described as a revenue-generating role. There are two main areas within front office: investment banking and markets.
a) Investment banking involves advising organizations on mergers and acquisitions, as well as a wide array of capital raising strategies.
b) Markets is divided into "sales and trading" (including "structuring"), and "research". -
2. Middle office
This area of the bank includes treasury management, internal controls (such as Risk), and internal corporate strategy.
Corporate treasury is responsible for an investment bank's funding, capital structure management, and liquidity risk monitoring; it is (co)responsible for the bank's funds transfer pricing (FTP) framework. -
3. Back office
The back office data-checks trades that have been conducted, ensuring that they are not wrong, and transacts the required transfers.
Many banks have outsourced operations. It is, however, a critical part of the bank
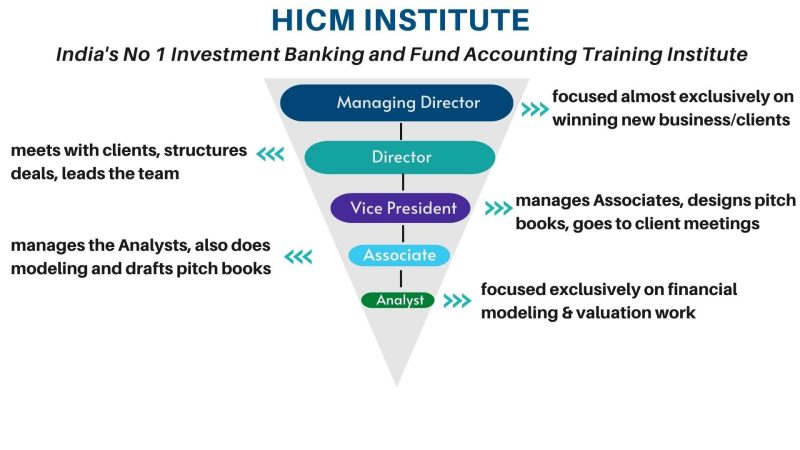
The course has been structured to give you the practical hands on along with the theoritical class


