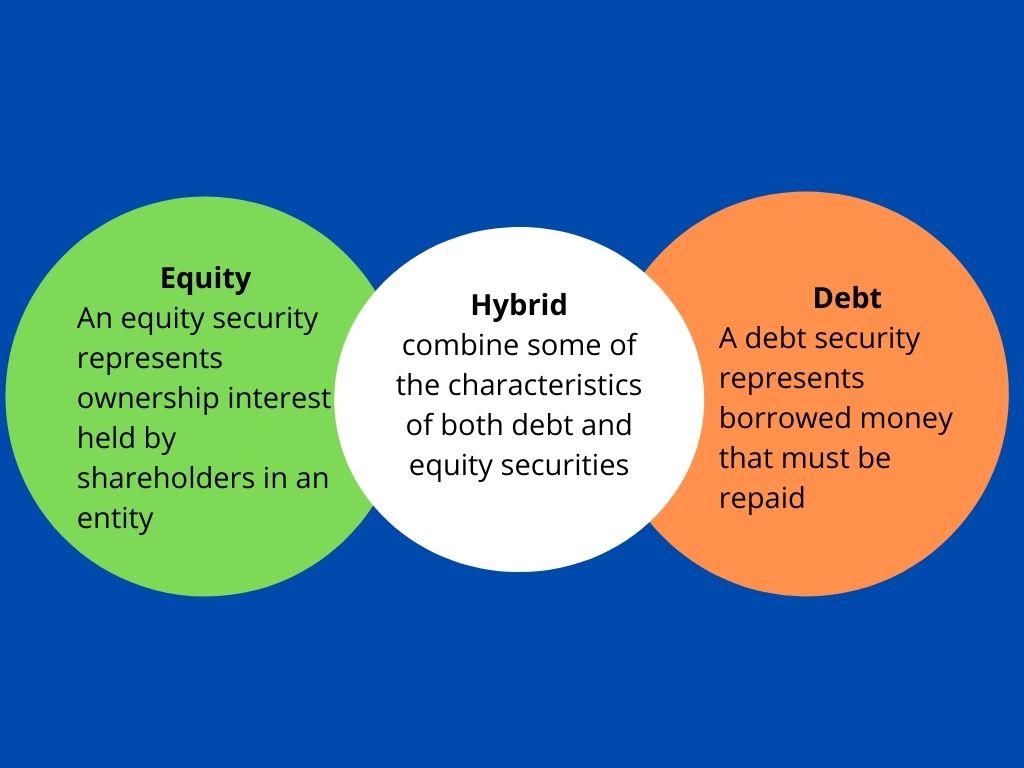
Difference Between Intraday and Delivery Trading
INTRADAY TRADING
What are intraday trades?
If you do not square off your position by the end of the day, your stock can be sold automatically at the day’s closing price under certain brokerage plans.
Most traders initiate an intraday trade by setting a target price for a stock and buying it if it is trading below the target price.
They then sell the stock if it reaches the target price or if they feel the stock won’t reach the target before the market closes for the day.
The motive behind trading shares intraday is to make quick profits within a day.
Low Capital
This way, they get to place a larger trade while paying only a small amount upfront.
Their broker provides the additional funds for the trade.
Thus, the trader is able to bet on a bigger position than his/her capital would allow. This pushes up the potential for profit as well.
High Liquidity
Time Limit
Intraday trades needs be be sqaured off at the end of each day.
Unimited Losses
No Overnight Risk
No Corporate benefits
DELIVERY TRADING
What are delivery trades?
Low Capital
They have to pay the full sum when buying stocks.
This entire amount remains blocked until the stock can be sold and limits the potential for big returns as well.
No leverage
No Time Limit
Limited Losses
Overnight Risk
Corporate benefits
Join Certification Courses

Certified Investment Banking
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Fund accounting
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Financial Analyst
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Business Analyst
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Wealth Manager
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Equity Dealer
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Trader
Duration= 2 Months

Certified Beta Trader
Duration= 2 Months
- Download brochure
- Register for demo class
- Course registration form
- Pay your fees now
Margins
What are Margins
What are different types of margins collected by stock exchanges?
Daily margins are collected to safeguard against eventualities that might occur between two trading days.
In the derivative segment, both the buyer and seller have to deposit initial margin before the opening of the day of the Futures transaction.
The margin is normally calculated taking into consideration changes in
This largely depends on the sharpness in the movement of share price or volumes, clientwise net outstanding purchase or sale position or on both sides.
The margin is calculated on the basis of difference between a particular day’s close and the previous day’s close. It is mostly applicable in the F&O segment.
The volatility margin is imposed to check abnormal intra-day fluctuations in any scrip. The objective is to ensure that buyers and sellers honour their commitments even if there are wild swings in share prices.
Volatility margin is generally calculated by working out the difference between the highest price and the lowest price over a 45-day transaction cycle and comparing it to the lowest price. The margin is paid in cash or in form of demat shares.

What is Record date

What is Book Closure
It the periodic closure of the Register of Members and Transfer Books of the company, to take a record of the shareholders to determine their entitlement to dividends or to bonus or right shares or any other rights pertaining to shares

What is trend line

What is trading of Partly Paid Shares and Debentures
MARKET MAKING
What is market making

Wanna work together?
SHORT SELLING
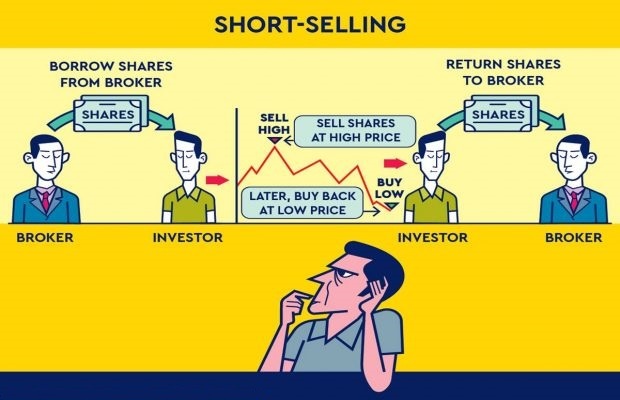
What is short selling shares?
FAQ’s on Settlement Cycle


Why Sell Short?
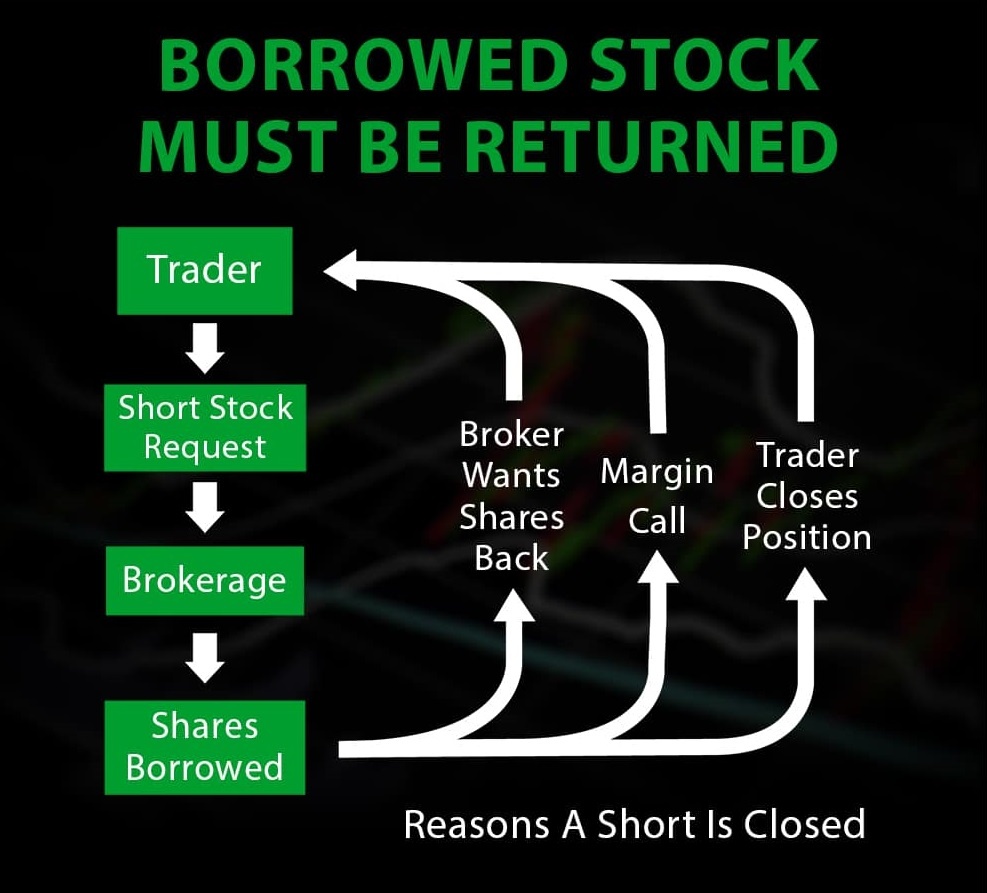
What happens after shares are borrowed
FAQ’s on Settlement Cycle
Pay-out day is the day the securities purchased are delivered to the buyers and the funds for the securities sold are given to the sellers by the exchange. At present, the pay-in and pay-out happens on the 2nd working day after the trade is executed on the exchange, that is settlement cycle is on T+2 rolling settlement.
Trading at BSE
BOMBAY STOCK EXCHANGE LTD.
It is a voluntary non-profit making Association of Persons (AOP) and is currently engaged in the process of converting itself into demutualised and corporate entity. It has evolved over the years into its present status as the premier Stock Exchange in the country.
It is the first Stock Exchange in the Country to have obtained permanent recognition in 1956 from the Govt. of India under the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956. The Exchange, provides market for trading in securities, debt and derivatives upholds the interests of the investors and ensures redressal of their grievances whether against the companies or its own member-brokers.
It also strives to educate and enlighten the investors by conducting investor education programmes and making available to them necessary informative inputs.
Trading at BSE
Settlement system at bse
Compulsory Rolling Settlement
The settlement calendar, which indicates the dates of the various settlement related activities, is drawn by BSE in advance and is circulated among the market participants.
Pay-in and Pay-out for A B T C F G Z group of securities
All deliveries of securities are required to be routed through the Clearing House. The Pay-in/Pay-out of funds based on the money statement and that of securities based on Delivery Order/ Receiver Order issued by BSE are settled on T+2 day.